The Anatomy of a DApp: Core Principles and Architecture
Are you ready to build the future of the internet? The digital world is evolving, and decentralized applications (DApps) are at its forefront. These innovative tools are changing how we interact online, offering the best transparency, security, and user control.
The global blockchain market is booming, expected to hit $69.04 billion by 2027. This creates incredible opportunities for developers ready to dive into Web3 and explore Specialized blockchain dapps development.
In this comprehensive guide, we will take you from the very basics of DApps to becoming a DApp hero. We will explore what DApps are, how they differ from traditional apps, and the core features that define them. We will then walk through the entire development process, from choosing the right blockchain platform to building, testing, and deploying your own DApp.
Our goal is to equip you with the knowledge and steps needed to navigate the exciting world of DApp development successfully.
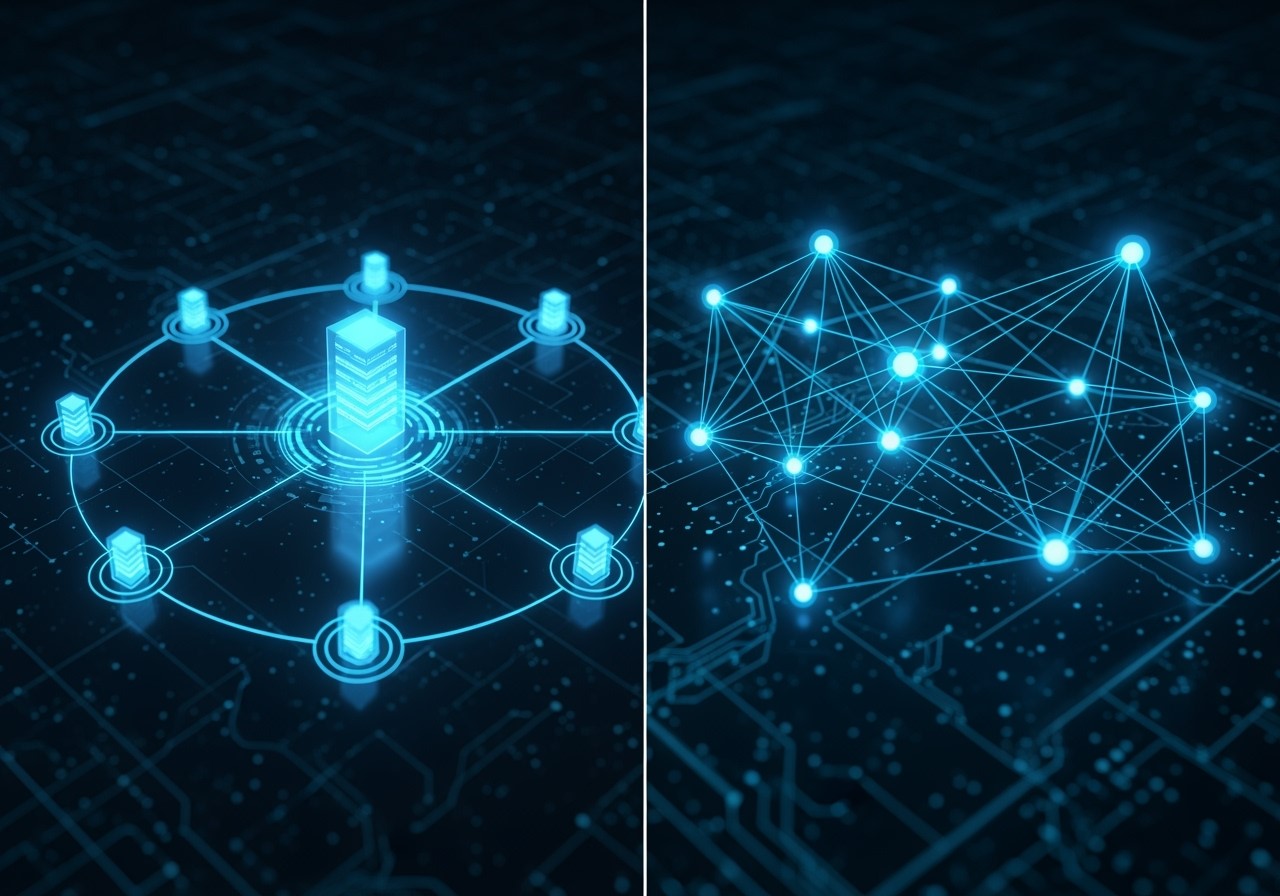
Decentralized applications (DApps) represent a fundamental shift from the traditional software models we’ve grown accustomed to. Instead of relying on centralized servers controlled by a single entity, DApps leverage blockchain technology and peer-to-peer networks. This profound architectural difference moves control from corporations to the community and individual users.
At its heart, a DApp is a software application that runs on a blockchain or a peer-to-peer network of computers. This means that its backend logic, data storage, and operations are distributed across many nodes, rather than housed in a single data center. This inherent distribution provides a robust foundation for improved security, transparency, and resilience.
The core components of a DApp typically include:
- Smart Contractsare self-executing programs that encapsulate the DApp’s business logic and run directly on the blockchain.
- Decentralized Frontend:While not always entirely decentralized, the user interface often interacts with the blockchain directly via Web3 libraries.
- Blockchain Network:The underlying infrastructure providing a decentralized transaction ledger and brilliant contract execution.
- Decentralized Storage (Optional but everyday):Solutions like IPFS or Arweave are often used to handle large amounts of data that are too expensive or impractical to store directly on the blockchain.
- Wallet Integration:This feature allows users to connect their cryptocurrency wallets (e.g., MetaMask) to interact with the DApp and sign transactions.
What Makes a DApp Different?
The defining characteristics of a DApp set it apart from its centralized counterparts:
- Open Source:The code for DApps is typically open-source, meaning anyone can inspect it. This fosters transparency and allows the community to verify its functionality and security.
- Decentralized:All records and operations are stored on a blockchain, a distributed ledger. This eliminates single points of failure and prevents a single entity from controlling or manipulating the data.
- Incentivized:Many DApps have built-in economic incentives, often through cryptographic tokens, that reward users for participating in and maintaining the network. This aligns users’ interests with the application’s.
- Protocol-compliant:DApps adhere to a specific blockchain’s protocols, which dictate how transactions are validated and data is stored. This ensures consistency and security across the network.
- Trustless Architecture:Users don’t need to trust a central authority to ensure the DApp functions as intended. The rules are enforced by code on the blockchain, and transactions are immutable and verifiable.
The Power of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are the backbone of DApps. They are self-executing agreements with the terms directly written into code, residing on a blockchain. Once deployed, they cannot be changed, ensuring their immutability and reliability.
These digital contracts act as the backend logic of a DApp. For instance, in a decentralized exchange, a smart contract would handle the logic for swapping tokens, ensuring that if you send one token, you automatically receive another, without any intermediary.
Solidity is the most common programming language for writing smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain (the platform that pioneered smart contracts). Developers use Solidity to define the rules, states, and functions of their DApps. Once compiled and deployed, this code executes automatically when certain conditions are met. This capability has led to a surge in Smart Contract Development and opened up new avenues for businesses looking to leverage Solidity Blockchain Business solutions.
Key Benefits for Users and Developers
The decentralized nature of DApps brings several compelling advantages:
- Censorship Resistance:Because DApps don’t have a central server, they are tough to shut down or censor. Unlike traditional platforms, if a social media DApp were built on a blockchain, no single entity could block your posts or ban your account. This ensures freedom of speech and access.
- Zero Downtime:Once a smart contract is deployed on the blockchain, it’s always accessible. There’s no server to go down, ensuring continuous availability. This eliminates the risk of service interruptions that plague centralized applications.
- Data Integrity:All data on a blockchain is immutable and cryptographically secured. Once information is recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted, ensuring the highest level of data integrity and trustworthiness.
- Improved Security:Decentralization inherently reduces single points of failure, making DApps less vulnerable to cyberattacks like denial-of-service (DoS) attacks. While smart contract vulnerabilities can exist, the underlying network is highly resilient.
- User Privacy and Control:Users often have greater control over their data and identity in DApps. Pseudonymity is common, and users typically own their digital assets and control access to their information through their cryptographic keys.
Your Blueprint for Blockchain Dapps Development
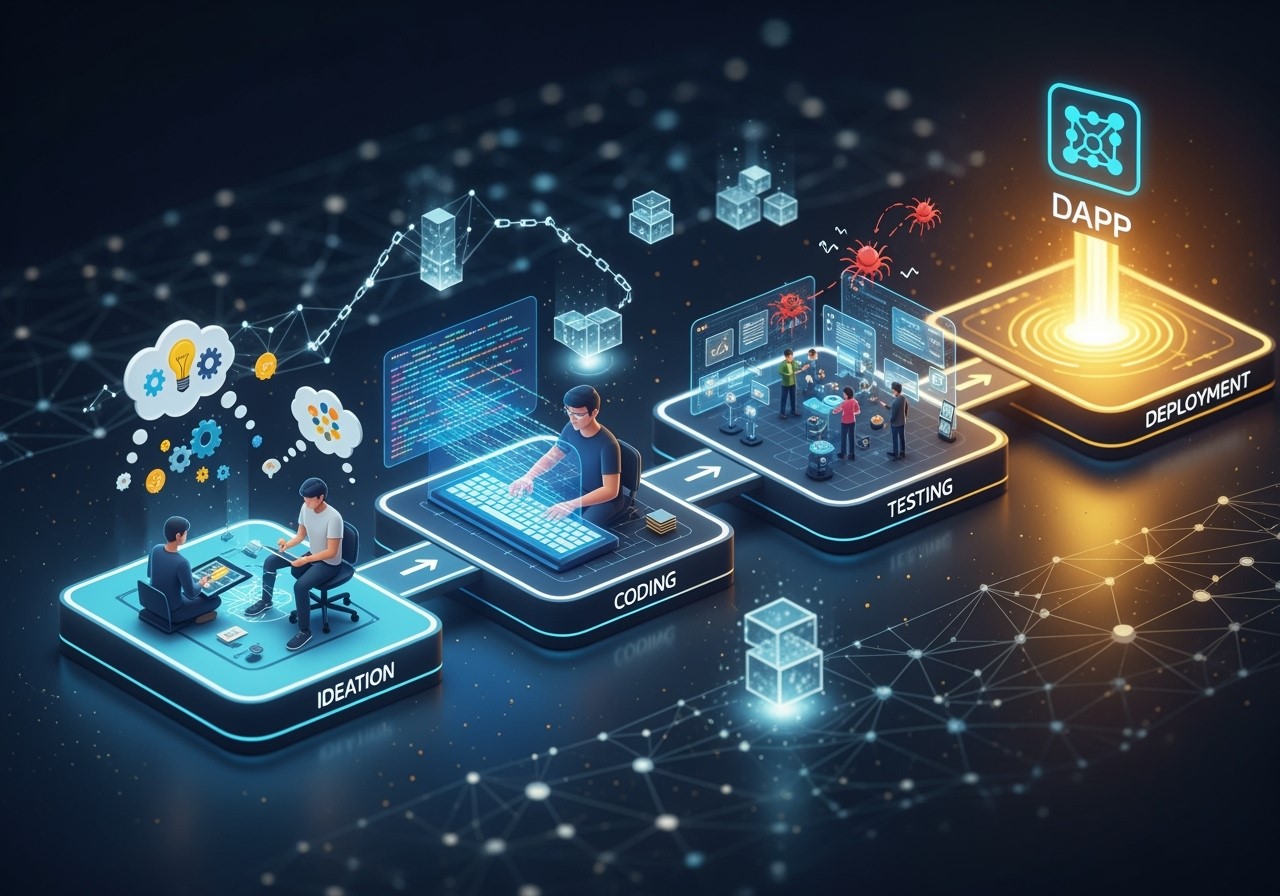
Starting on DApp development can seem daunting, but we can steer the process effectively by breaking it down into manageable steps. Think of this as your blueprint for building a decentralized future.
Step 1: Ideation and Proof-of-Concept (PoC)
Every great DApp starts with a compelling idea. This initial phase is crucial for laying a solid foundation.
- Problem Identification:What real-world problem are you trying to solve? How can blockchain technology offer a superior solution compared to traditional methods? Understanding your audience’s pain points is paramount.
- Whitepaper Creation:A whitepaper outlines your DApp’s vision, technical architecture, tokenomics (if applicable), and roadmap. It serves as a foundational document for your project.
- Feasibility Analysis:Can your idea be realistically implemented on a blockchain? What are the technical constraints, and what resources will be required?
- Defining the Core Value Proposition:Clearly articulate what unique value your DApp brings to users and the ecosystem. What makes it stand out?
Step 2: Choosing Your Blockchain Platform
Selecting the right blockchain platform is one of the most critical decisions in DApp development. Each platform has its strengths, weaknesses, and a unique ecosystem.
Here’s a brief comparison of some popular choices:
- Feature Ethereum Solana Polygon Speed~15-30 Transactions Per Second (TPS) 65,000+ TPS Up to 7,000 TPS Cost High gas fees ($0.50-$5+ per transaction), fluctuating heavily Ultra-low, average $0.00025 per transaction Low, typically a fraction of Ethereum’s fees Ecosystem Largest and most mature, extensive developer tools, strong community Growing rapidly, strong focus on high-performance applications Ethereum Layer-2, benefits from Ethereum’s security while improving scalability Consensus Proof-of-Stake (PoS) Proof-of-History (PoH) + Proof-of-Stake (PoS) Proof-of-Stake (PoS) Consensus Mechanisms: Understand how each blockchain validates transactions (e.g., Proof-of-Work, Proof-of-Stake, Proof-of-History). This impacts security, speed, and energy consumption.
- Scalability Trilemma:No blockchain perfectly achieves decentralization, security, and scalability simultaneously. You’ll need to prioritize based on your DApp’s needs. For instance, while Ethereum boasts the largest DApp ecosystem with over 3,500 DApps and daily active users approaching 160k as of May 2021, its scalability challenges have led to the rise of Layer-2 solutions like Ethereum Layer 2 Rollups Faster Transactions. Other platforms like Solana Blockchain Efficiency and EOS Blockchain Advantages offer different trade-offs.
- Developer Community:A vibrant developer community means more resources, tools, and support. Ethereum, for example, has a massive and active developer base.
Step 3: Assembling Your Development Toolkit
Once you’ve chosen your platform, you’ll need the right tools to build your DApp. The Web3 development ecosystem is rich and constantly evolving, offering robust frameworks and libraries. To explore the tools available, explore various Web3 Development Frameworks.
Here are some essential tools you’ll likely encounter:
- js & NPM (Node Package Manager):Node.js is a JavaScript runtime that is vital in managing your project’s packages and dependencies. NPM (or Yarn) is used to install and manage these packages.
- Truffle Frameworkis a popular development environment, testing framework, and asset pipeline for blockchains using the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). It simplifies brilliant contract compilation, deployment, and testing.
- Hardhat:Another widely used Ethereum development environment that offers flexibility, extensibility, and features like a local Ethereum network for testing and debugging.
- Ganache:A personal Ethereum blockchain that you can use to run tests, deploy contracts, and develop your DApps. Ganache provides a visual interface and pre-funded accounts, making local development easy.
- MetaMask:A browser extension that serves as a cryptocurrency wallet and a gateway to interact with DApps. MetaMask allows users to manage their accounts, sign transactions, and connect to DApps.
- js / Web3.js:JavaScript libraries that enable your frontend application to interact with the blockchain. Web3.js (or Ethers.js) abstracts the complex JSON-RPC calls to communicate with an Ethereum node.
Step 4: Building, Testing, and Auditing
With your concept clear and tools ready, it’s time to build.
- Frontend Developmentinvolves creating the user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) for your DApp. Popular JavaScript libraries like React and Vue are commonly used to build responsive and interactive interfaces that connect to your smart contracts.
- Clever Contract Coding:Write your smart contracts using Solidity (or other appropriate language for your chosen blockchain). This is where the core logic of your DApp resides. Ensure your code is clean, efficient, and follows best practices to minimize gas costs and potential vulnerabilities.
- Unit Testing:Test individual functions and components of your smart contracts to ensure they behave as expected. Tools like Truffle and Hardhat have built-in testing frameworks (e.g., Mocha and Chai). Thorough testing is paramount, as deployed smart contracts are immutable. Learn more about Basic Debugging Techniques Truffle Development.
- Integration Testing:Verify that different parts of your DApp (frontend, smart contracts, wallet) work seamlessly together.
- The Importance of Security Audits:Given the immutability of smart contracts and the financial value often associated with DApps, security audits are non-negotiable. Independent third-party auditors review your code for vulnerabilities like reentrancy, frontrunning, and integer overflows. This rigorous scrutiny is critical to prevent exploits, as demonstrated by the over $3.8 billion lost to DeFi exploits in 2022. For comprehensive security, consider a Smart Contract Audit. Engaging in Specialized blockchain dapps development with experienced teams can provide the necessary expertise and rigorous auditing processes for those looking to build robust and secure decentralized applications.
Navigating the Real-World Challenges of DApp Development
While DApps offer immense potential, their development comes with unique challenges that developers must address. Understanding these problems from the outset can help you build more resilient and user-friendly applications.
Overcoming Technical Problems
- Scalability Solutions:Blockchains, especially older ones like Ethereum, can face congestion and slow transaction speeds (around 15-30 TPS). This impacts user experience and increases costs. Solutions like Layer-2 rollups (e.g., Optimism, Arbitrum on Ethereum) process transactions off-chain, then bundle them back to the mainnet, significantly increasing throughput. Newer blockchains like Solana boast speeds of 65,000+ TPS and ultra-low transaction costs, providing an alternative for high-performance DApps.
- User Experience (UX) Complexity:Traditional apps are often intuitive, but DApps can present a steep learning curve for new users. Concepts like gas fees, wallet management, and transaction confirmations can be confusing. Designing for simplicity, providing clear feedback, and abstracting blockchain complexities where possible are crucial for broader adoption.
- Wallet Integration:Seamlessly integrating various cryptocurrency wallets is essential for user access. Developers need to ensure compatibility and a smooth connection process.
- On-chain vs. Off-chain Data:Storing all data directly on a blockchain is expensive and inefficient for large datasets. Developers must strategically decide what data resides on-chain (critical, immutable data) and what can be stored off-chain (e.g., using decentralized storage solutions like IPFS) while maintaining data integrity.
Understanding the Cost of Blockchain Dapps Development
The cost of DApp development can vary widely, much like traditional software development, but with added blockchain-specific factors.
- Project Complexity:A simple DApp like a voting system might cost between $5,000 and $10,000, while a complex DeFi lending protocol could easily exceed $100,000-$150,000+. The number of features, smart contract complexity, and integrations directly impact the price.
- Development Team:Hiring an in-house team, freelancing, or outsourcing to a specialized agency will have different cost implications. Rates vary significantly based on location and expertise.
- Smart Contract Audits:Professional security audits are a significant but necessary expense, ranging from several thousand to tens of thousands of dollars, depending on the contract’s complexity. These audits are vital to prevent costly exploits.
- Ongoing Maintenance:DApps require continuous monitoring, updates, and potential bug fixes, especially as the underlying blockchain technology evolves.
Real-World DApp Examples and Use Cases
DApps are already making a significant impact across various industries, showcasing the power of decentralization. Explore decentralized applications to gain a broader understanding of how these applications function and their impact.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi):DApps like Uniswap (a decentralized exchange for token swaps) and Aave (a lending and borrowing protocol) have revolutionized financial services. They offer transparent, permissionless access to financial tools, bypassing traditional intermediaries.
- Gaming:Play-to-earn games like Axie Infinity and Splinterlands allow players to own in-game assets as NFTs and earn cryptocurrency rewards, creating player-owned economies.
- Non-fungible tokens (NFTs):Marketplaces like OpenSea are DApps that facilitate the buying, selling, and trading of unique digital assets, from art to collectibles.
- Supply Chain Management:DApps can provide improved traceability and transparency for goods moving through a supply chain, from production to delivery, reducing fraud and increasing efficiency.
- Decentralized Identity:DApps are emerging to give users sovereign control over their digital identities, allowing them to share credentials selectively without relying on central authorities.
Frequently Asked Questions about DApp Development
As you learn more about DApp development, certain questions will arise. Let’s address some of the most common ones.
How much does it cost to build a DApp?
The cost to build a DApp is highly variable, depending on numerous factors. A basic DApp with minimal functionality might start from around $5,000 to $10,000. However, for more complex DApps, such as a DeFi lending platform or a sophisticated NFT marketplace, costs can easily range from $50,000 to over $150,000.
Key factors influencing the price include:
- Project Complexity:The number of features, the intricacy of smart contracts, and the need for custom logic.
- Blockchain Choice:Different platforms may require different development expertise and have varying transaction costs for deployment.
- Development Team:Whether you hire freelancers, an in-house team, or a specialized DApp development agency.
- Smart Contract Audits:A crucial but costly step to ensure security.
- Frontend Design & Development:The complexity of the user interface and overall user experience.
- Post-launch Costs:Ongoing maintenance, security monitoring, and potential upgrades.
Which blockchain is best for DApp development?
There isn’t a single “best” blockchain for DApp development; the ideal choice depends entirely on your project’s specific requirements and priorities.
- Ethereumremains the most popular and battle-tested platform, with the largest ecosystem, developer community, and robust tooling. It offers unparalleled security and decentralization but comes with higher transaction fees and lower scalability (though Layer-2 solutions are addressing this).
- Solana:Known for its high transaction throughput (TPS) and extremely low fees, it is suitable for DApps requiring high speed and frequent interactions, such as gaming or high-frequency trading.
- Polygon:An Ethereum Layer-2 scaling solution, offering compatibility with Ethereum’s tools and ecosystem while providing significantly lower fees and faster transactions. It’s an excellent choice for DApps that need to scale while benefiting from Ethereum’s security.
- Other Platforms, such asBinance Smart Chain, Cardano, TRON, EOS, and Avalanche, also offer viable alternatives. Each has distinct features, consensus mechanisms, and developer communities.
You need to assess your DApp’s needs regarding transaction speed, cost, security, decentralization, and the existing user base to make an informed decision.
Can I build a DApp without any coding experience?
While it’s possible to start with DApp development using some “no-code” or “low-code” platforms and tools, building a fully functional, secure, and complex DApp typically requires significant coding experience.
- No-Code Platforms:Tools like thirdweb and Moralis offer simplified interfaces and pre-built components that help non-developers deploy basic smart contracts or integrate Web3 functionalities into existing applications. These can be great for prototyping or simpler use cases.
- Technical Requirements:Even with these tools, a basic understanding of blockchain concepts, smart contracts, and how Web3 works is beneficial. For anything beyond the most rudimentary DApp, knowledge of programming languages like Solidity (for smart contracts) and JavaScript (for frontend interaction) is essential.
- The Role of Developers:For robust, custom DApps with unique logic, complex integrations, and stringent security requirements, experienced blockchain developers are indispensable. They ensure the smart contracts are secure, efficient, and optimized, and that the entire DApp architecture is sound.
Conclusion: Your Journey into Web3 Begins Now
We’ve journeyed from understanding the fundamental concepts of decentralized applications to outlining the practical steps involved in their development. We’ve seen how DApps differ from traditional software, leveraged by the immutable power of smart contracts and blockchain technology, offering unprecedented transparency, security, and user control benefits.
Becoming a DApp hero involves careful planning, strategic platform selection, mastering development tools, and a commitment to rigorous testing and auditing. While challenges like scalability and user experience exist, the rapid evolution of the Web3 ecosystem continually provides innovative solutions.
The global blockchain market is on an exponential growth trajectory, and DApps are at the heart of this revolution. Your journey into Web3 development is not just about writing code; it’s about contributing to a more open, transparent, and user-centric internet. The opportunities are vast, and the impact you can make is significant.
Are you ready to build the next generation of digital experiences? The future awaits your innovation. Visit our dedicated page on decentralized applications to explore how you can contribute to this exciting future.