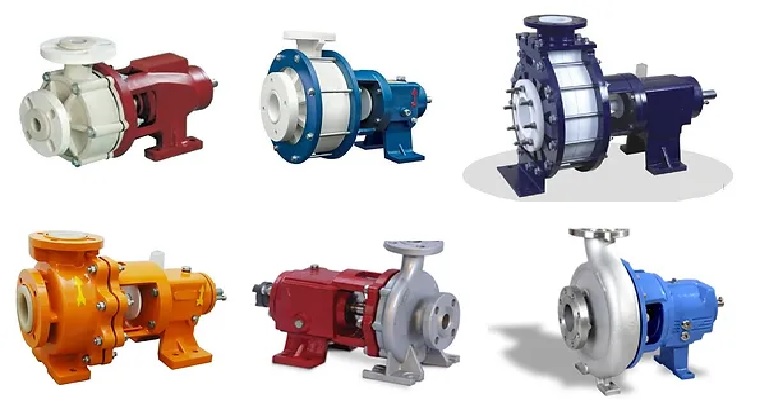
Sludge pumps play a vital role in industries and municipal settings by efficiently handling and transferring silt, a semi-solid waste material. These pumps are designed to overcome challenges such as high viscosity, abrasive nature, and potential clogging. Embark on exploring sludge pumps for sale, delving into their purpose, components, and operational principles in this comprehensive article.
Unravelling the Role of Sludge Pumps
Sludge pumps, particularly electric ones, are essential for efficiently transporting and disposing of silt, which comprises solids suspended in a liquid medium. This waste material is generated in various applications such as wastewater treatment plants, industrial processes, mining operations, and dredging activities. An electric sludge pump is crucial in removing silts from its source and their subsequent transfer to treatment facilities or disposal sites. By effectively managing them, these pumps significantly contribute to upholding environmental and public health standards in industrial and municipal settings.
Types of Sludge Pumps
The different sludge pump types commonly used, including centrifugal pumps, positive displacement pumps, and submersible pumps, offer various capabilities and are designed to handle specific silt characteristics and applications, considering factors such as sludge pump price. Centrifugal pumps are well-suited for transferring large volumes of sediments with low to medium viscosity. In contrast, positive displacement pumps excel in handling high-viscosity sediment and meeting precise flow rate requirements. Submersible pumps, on the other hand, are submerged in filth and can effectively operate at varying liquid depths.
Components of the Pump
1. Motor: At the heart of a sludge pump lies an electric or hydraulic motor that provides the necessary power to drive the pump’s operation. The motor is designed to withstand the demanding conditions encountered in sediment handling applications.
2. Impeller: The impeller is a crucial component responsible for generating the hydraulic energy required to move sediment through the pump. Within the pump casing, vanes or blades rotate, generating centrifugal force and propelling the sediment in a forward direction.
3. Pump Casing: The pump casing houses the impeller and directs the silt flow. It is designed to withstand its corrosive and abrasive nature and often incorporates wear-resistant materials to extend its lifespan. It is also typically equipped with robust sealing mechanisms to prevent leakage and ensure efficient sediment flow management.
4. Sealing Mechanism: Sump pumps feature robust sealing systems to prevent leakage and protect the motor from contact with the slurry. Depending on the specific pump design, common sealing mechanisms include mechanical seals, packing glands, or lip seals.
Their Operational Principles
1. Priming: Sump pumps require priming before an operation to eliminate air in the pump or suction line, which can hinder the pumping process. Priming involves filling the pump casing and suction pipe with mud to ensure the impeller is fully immersed, enabling efficient pumping.
2. Suction and Discharge: These pumps use suction to draw sediment into the pump casing. The impeller then imparts kinetic energy to the silt, propelling it towards the discharge outlet. The filth is expelled through the discharge pipe, overcoming resistance caused by friction and gravity.
3. Viscosity and Solid Handling: Silt often exhibits high viscosity due to its semi-solid nature. To handle such challenging fluids, sump pumps are designed with larger clearances between the impeller and casing, allowing for the passage of solids without clogging. Some pumps may also incorporate features like augers or macerators to break down solid particles further and enhance pumping efficiency.
4. Pump Selection: The selection of a sump pump, including a small sludge pump, depends on various factors, including the characteristics of the sediment (viscosity, solids content), required flow rate, head pressure, and the distance and elevation of its transfer. Different pump types, such as centrifugal pumps, positive displacement pumps, or submersible pumps, cater to different applications and operational requirements.
Conclusion
Ongoing advancements in pump technology have led to notable enhancements in the efficiency, durability, and performance of sludge pumps for sale. Innovations like improved impeller designs, wear-resistant materials, and advanced sealing mechanisms have enabled more efficient handling of highly viscous and solid-laden silt. These developments have increased reliability, reduced maintenance needs, and improved energy efficiency. Understanding sump pump components and operational principles empower industries and municipalities to choose the right pump type for effective silt management, ensuring optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.