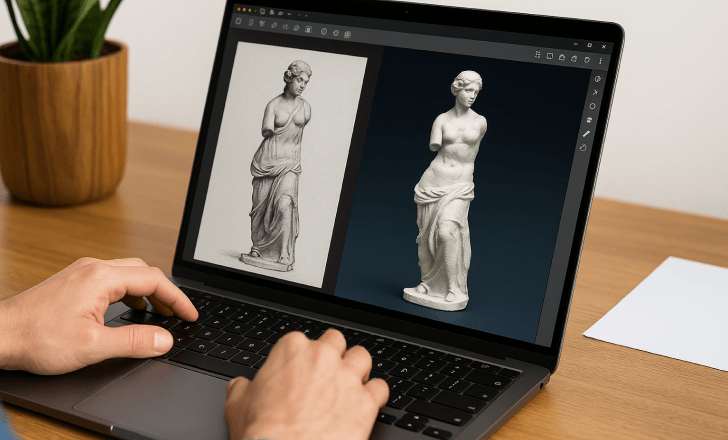
Creative teams across the United States creative market are moving faster with 2D to 3D conversion. Instead of spending weeks on manual modeling or full scans, you can build depth-rich scenes in hours. With Hyper3D Image to 3d and the Vidu AI video generator, flat photos become immersive visuals and animated clips ready for web, AR, and video.
This guide shows how depth mapping leads to clean mesh generation, smart textures, and a smooth 3D animation workflow. You will learn the AI 3D pipeline from source image prep to lighting basics and export steps. We also touch on photogrammetry alternatives that cut cost while keeping quality for marketing, e-commerce, and social media.
Expect clear steps, pro tips, and tools that fit real production. We cover hardware, software, and file formats, plus integrations with Unreal Engine, Unity, and Blender. By the end, you will know how to link Hyper3D Image to 3d with the Vidu AI video generator to turn stills into motion, publish with confidence, and scale your workflow without heavy overhead.
Why Turning 2D Images into 3D Is Changing Creative Workflows
Converting flat photos into depthrich scenes is reshaping creative workflows by shrinking the path from idea to onscreen. With AI depth estimation, teams move from sketches to previews in hours, not weeks. A single image becomes a parallax scene, a product spin, or a motion shot without heavy modeling.
This shift unlocks speed and scale. The 2D to 3D pipeline lets small studios test more concepts and swap angles fast. Real-time rendering in Unreal Engine or Unity makes edits visible on the spot, so feedback loops get shorter and budgets stay under control.
Retail and media gain new ways to engage. Interactive product visuals power zoomable spins and AR tryons that hold attention on Shopify, Instagram, and TikTok. Immersive marketing benefits from reusable assets—one scene can ship to web, mobile, and YouTube Shorts with minimal rework.
Film and TV embrace virtual production with imagebased sets for previz and quick set extensions. Blender and Adobe After Effects handle compositing and polish, while the same assets feed into real-time rendering for live demos and pitches. The result is flexible delivery without a full rebuild.
For ad testing, the 2D to 3D pipeline enables rapid A/B variants—new lighting, focal length, or camera moves—guided by AI depth estimation. Teams iterate faster, keep brand style tight, and hit timelines even when products or scenes change midcampaign.
Essential Tools and Requirements for High-Quality 3D Conversion
Turning flat images into depth-rich scenes calls for balanced hardware, smart software choices, and clean files. Match your GPU requirements to project scale, keep color consistent, and favor formats that hold precision from start to finish. This approach pays off in Blender, Unreal Engine, and Unity alike.
Hardware considerations for smoother rendering
A modern multicore CPU, such as AMD Ryzen 7/9 or Intel Core i7/i9, speeds up depth estimation and baking. Pair it with an NVIDIA RTX card to leverage NVIDIA CUDA and OptiX in Blender Cycles and many AI tools. For mobile rigs, Apple Silicon with Metal support delivers strong viewport and encode performance.
Start with 32 GB RAM for highresolution textures; 64 GB or more keeps large scenes responsive. Use NVMe SSDs on PCIe 3.0/4.0 for fast caches and texture streaming. A calibrated sRGB or DCIP3 monitor helps you judge PBR materials and HDRI lighting without surprises.
Recommended software and plugins for beginners and pros
Blender covers modeling, UVs, and rendering, while Unreal Engine and Unity shine for realtime previews and interactivity. Adobe Substance 3D Painter and Sampler boost material realism with PBR maps and smart masks. For upscale and cleanup, use Topaz Gigapixel AI or the Super Resolution feature in Adobe Photoshop.
Round out the pipeline with DaVinci Resolve or After Effects for grading and motion. Pull HDRI environments from trusted libraries to light scenes fast, then swap or rotate them to test mood and reflections without complex rigs.
File formats and image resolution best practices
For source images, favor highresolution PNG or TIFF with minimal compression. Aim for 3000–6000 pixels on the long edge to protect detail during displacement and closeups. For depth data, write 16bit grayscale PNG or OpenEXR to avoid banding and preserve subtle gradients.
Keep PBR texture sets organized: Base Color, Roughness, Metallic, Normal, and Height at 8–16 bit as needed. Use HDRI EXR files for consistent lighting and linear color workflows. Export GLB/GLTF for web and AR, FBX or OBJ for DCC tools and engines, and USD/USDZ for Apple pipelines.
Hyper3D Image to 3d,Vidu AI video generator
Bring flat visuals to life with a fast, practical path. Hyper3D Image to 3d infers depth from a single frame or a small set, while the Vidu AI video generator turns those results into camera-ready motion. Teams get crisp detail, clean edges, and fewer artifacts during moves, which means smoother post-production.
Tip: Keep your source image clean and well lit. Strong contrast helps the AI depth map lock onto contours for better mesh reconstruction and stable motion parallax.
How Hyper3D accelerates photorealistic depth mapping
Hyper3D Image to 3d produces an AI depth map with perceptually sharp edges and improved occlusion handling. It exports depth-driven meshes and displacement-ready maps that drop into Blender, Unreal Engine, and Unity. The mesh reconstruction is fast, so you spend less time fixing silhouettes and more time on look dev.
Because the depth is consistent, camera push-ins feel natural. You can stage lighting early, then refine materials without redoing geometry. This reduces cleanup and keeps motion parallax stable during tests.
Turning 3D outputs into dynamic clips with Vidu AI
The Vidu AI video generator ingests depth-based scenes and turns them into a cinematic AI video with ease. Set keyframes for orbit shots, push-ins, or rack focus, then dial motion blur and depth of field. You can match brand tone through color, grain, and pacing, and prepare aspect ratios for 9:16, 1:1, and 16:9 in one pass.
Creators keep fidelity by rendering layers or sending the mesh directly. The result is a polished sequence that is ready for post-production and quick revisions.
Workflow synergy: from stills to cinematic motion
Start with Hyper3D Image to 3d to build a depth-rich base, refine textures and lights in a DCC, then move into the Vidu AI video generator for timing and camera paths. The combo shortens delivery while preserving detail, making motion parallax feel grounded instead of fake.
For scale, use batch exports, shared LUTs, HDRIs, and camera presets. This keeps a unified look across a catalog and speeds post-production on every cinematic AI video you ship.
Step-by-Step Workflow: From Flat Image to Depth-Rich 3D
Start with a clear plan. Keep the source image sharp, the geometry tidy, and the output lean. The path below guides you from careful image cleanup to exports ready for web, AR, and social video formats.
Preparing your source image and cleaning artifacts
Use the highest-resolution file you can find. In Adobe Camera Raw or Topaz Denoise AI, remove noise, fix chromatic aberration, and even out tones. Perform precise image cleanup: erase dust, heal cloning seams, and correct edge halos.
Separate subject and background into layers for control. Mask hair and fine edges with care to avoid halos later. Save a pristine working copy before you move to depth map refinement.
Generating depth maps and refining surface geometry
Create a 16-bit depth map in Hyper3D and export PNG or EXR to reduce banding. In Blender, apply the map as displacement on a subdivided plane, or build a mesh with geometry nodes. Focus depth map refinement around hair, silhouettes, and strong specular areas.
Sculpt problem zones to smooth ridges and fix overlaps. Retopologize if the mesh deforms poorly or you need faster playback. A clean topology gives better results with subtle camera motion and DOF.
Texturing, lighting, and camera setup for realism
Build PBR texturing from the original diffuse. Use Substance 3D Sampler or Materialize to derive Normal and Roughness maps. Add HDRI lighting for a believable base, then shape with key, fill, and rim lights.
Match real camera choices: a 35–85 mm focal length for portraits, aperture to set DOF, and filmic tone mapping for range. Add a gentle dolly or parallax move to show displacement depth without breaking the scene.
Exporting for web, AR, and video platforms
For web and AR, export GLB/GLTF with Basis/ktx2 textures and keep packages under 10–20 MB. For iOS, export USDZ and confirm materials and AO bake correctly. Check gamma and color space so assets match across apps.
For video masters, render Apple ProRes 422 or 4444, or Avid DNxHR. Deliver H.264 or H.265 in platform-native sizes: 1080×1920 for vertical feeds and 1920×1080 for widescreen. Include alpha when needed for composites and ensure timing fits social video formats.
Creative Use Cases: Marketing, E-commerce, and Social Media
Retail teams turn flat photos into shoppable 3D that invites touch-like browsing. On product detail pages, smooth product spins reveal stitching, finishes, and scale, building trust and driving a measurable conversion lift. With Hyper3D feeding Vidu AI, those same assets become quick hero loops that highlight materials under different lights.
Try-before-you-buy goes mainstream with AR try-on and room views using GLB or USDZ. Furniture, footwear, eyewear, and home decor brands publish one master scene that adapts to iOS and Android. Customers see fit and color in context, which reduces returns and boosts confidence at checkout.
For media buyers, short-form video built from depth-aware stills fuels efficient social ads. Subtle parallax and camera moves outperform static tiles, nudging higher thumb-stop rates and stronger completion. Lifestyle mockups evolve into stylized 2.5D sets that swap seasons, props, and backgrounds in minutes.
Studios and publishers repurpose the same scene across email banners, landing pages, reels, and DOOH. Explainer cuts and teaser shots match broadcast pacing while keeping brand presets intact. The result is rapid variant testing with fewer reshoots and a cleaner asset library.
Merchandisers use product spins for PDPs, then hand off depth-enhanced stills for retargeting edits. Social teams stitch short-form video with captions, while AR try-on supports in-store mirrors and WebAR. This unified flow preserves color, lighting, and typography for consistent storytelling.
From Nike-style footwear previews to IKEA-grade room planners, shoppable 3D and AR try-on meet shoppers where they browse. Lifestyle mockups power seasonal refreshes, social ads keep feeds lively, and each piece ladders to a conversion lift without adding new shoots. One pipeline, many outputs, strong ROI.
Optimizing Quality: Lighting, Textures, and Depth Precision
Great 3D starts with clear intent. Match the scene’s mood to the original image, keep materials consistent in a PBR workflow, and verify depth data before final renders. Balance clarity and speed with smart choices that hold up on web, AR, and video.
Choosing lighting rigs for mood and clarity
Begin with HDRI domes for believable ambient light, then layer a three-point lighting setup. Use a key to shape form, a fill to lift shadows, and a rim for crisp separation. Tune color temperature and exposure to match photo cues, and prefer area lights for soft, natural falloff.
Add gobos for texture and subtle patterning. Validate shadows and highlights against your reference, and keep speculars clean with proper roughness values. This discipline reduces harsh edges and supports artifact reduction before post work.
Texture baking versus real-time materials
Choose texture baking when you need stable looks across devices. Bake normal, ambient occlusion, and curvature to cut runtime costs and ensure consistent shading. Generate mipmaps and use ktx2 or Basis compression for fast, crisp web delivery without shimmer.
Opt for real-time materials in Unreal Engine or Unity when interactive control matters. Keep albedo linear, normals in the correct space, and metal/rough packed to save memory. In both paths, a clean PBR workflow preserves detail and minimizes surprises under different lights.
Avoiding common issues: stretching, noise, and banding
Fix UV stretching by relaxing shells and adding support geometry where depth changes fast. Render with balanced samples, then denoise carefully—OptiX in Blender is strong—while guarding fine textures from over-smoothing. Edge halos fade when you feather masks and refine depth normals.
Prevent banding by working with 16-bit depth or EXR; add subtle dithering if gradients step. Calibrate gamma, color space, and tone mapping so edits track the source intent. These checks tighten edges, improve artifact reduction, and keep gradients smooth end to end.
Integrations and Pipelines for Fast Production
Move Hyper3D results into a production-ready flow by treating depth maps as first-class assets. Start in Blender to convert depth to clean meshes, pack textures, and standardize names. Export FBX or GLB and hand off to Unreal Engine or Unity with consistent scale and units so shots match across teams.
Keep the Blender pipeline lean. Import the depth map as displacement or generate geometry, then apply PBR textures. For Unreal Engine, use packed ORM, enable virtual textures for large environments, and set Nanite where suitable. In Unity, map channels in HDRP or URP correctly, test on mobile and desktop, and profile memory early.
Connecting Hyper3D outputs to Unreal, Unity, and Blender
In Blender, create meshes from depth, unwrap UVs, and verify normals before export. Save FBX/GLB with meters and apply transforms. In Unreal Engine, script material instances for ORM, hook up normal maps, and set LODs for open worlds. In Unity, build materials per pipeline, tune lightmaps or light probes, and confirm reflection probes for metal and glass.
Automations with scripts and batch processing
Use Blender Python scripts to batch depth-to-mesh conversion, auto UV unwrap, and assign textures by filename. Trigger command-line batch rendering for preview passes and dailies. In Unreal Engine, rely on Editor Utility Widgets to batch import, generate LODs, and spawn material variants; in Unity, apply C# tools for batch rendering and prefab setup.
For motion, route rendered sequences to the Vidu AI video generator. Automate camera moves, aspect ratio variants, and safe-frame guides so delivery fits social, web, and broadcast without manual tweaks.
Version control and asset management tips
Adopt Git LFS or Perforce to store large binaries, including textures, HDRIs, and caches. Enforce semantic versioning on scenes and renders. Maintain shared asset libraries with standard HDRIs, LUTs, materials, and camera presets to keep brand looks stable across shots.
Scale with a render farm or cloud GPUs for heavy batch rendering. Document each step in a project wiki so onboarding stays fast, handoffs stay clean, and the Blender pipeline, Unreal Engine builds, and Unity exports remain predictable over time.
SEO and Distribution: Publishing 3D and Video Content That Ranks
To help immersive work reach more people in the United States, start with speed. Keep GLB and GLTF lean with texture compression and efficient meshes to boost WebGL performance and pass Core Web Vitals. Use lazy loading in your viewer to delay heavy assets. Name files with clear terms, add descriptive alt text, and keep titles natural for strong 3D SEO. Create high-quality thumbnails that match the scene’s promise and encourage clicks without bait.
Give search engines clear context with schema markup. Add JSON-LD for VideoObject on clips and Product for e-commerce, filling in name, description, thumbnailUrl, uploadDate, and contentUrl. Pair videos with captions and transcripts to improve accessibility and watch time, and support video SEO on platforms like YouTube. Produce multiple aspect ratios—16:9, 1:1, and 9:16—to fit Instagram, TikTok, LinkedIn, and X while keeping messaging consistent.
Strengthen discoverability with dedicated sitemaps for images and videos, and label AR assets with GLB or USDZ plus a clear call to action and device notes. Host 3D in a performant WebGL viewer, then repurpose core scenes into short clips using Vidu AI to widen reach. Track results in Google Analytics 4 and Search Console, and iterate fast with the Hyper3D Image to 3d pipeline to respond to search trends and campaign data. Steady updates, clean structure, and fast pages compound visibility over time.
FAQ
How do Hyper3D Image to 3d and the Vidu AI video generator work together?
Hyper3D quickly infers a high-fidelity depth map and base mesh from a single image. You refine textures and lighting in Blender, Unreal Engine, or Unity, then hand off the scene or renders to Vidu AI to create dynamic camera moves, aspect ratio versions, and polished clips for ads and social media.
Why is 2D-to-3D faster than traditional modeling or photogrammetry?
AI depth mapping automates geometry creation, cutting days of manual work into hours. You get clean parallax, solid occlusion handling, and ready-to-edit meshes without multi-shot capture or complex retopo pipelines, ideal for marketing, e-commerce, AR, and virtual production.
What hardware do I need for smooth 3D conversion and rendering?
Aim for an AMD Ryzen 7/9 or Intel Core i7/i9, an NVIDIA RTX 3060–4090 or Apple Silicon M1/M2/M3, 32–64 GB RAM, and fast NVMe SSD storage. A color-accurate sRGB or DCI-P3 monitor with hardware calibration helps keep grading consistent.
Which software stack is best for beginners and pros?
Use Blender for modeling, UVs, and rendering; Unreal Engine or Unity for real-time; Adobe Substance 3D for PBR materials; After Effects or DaVinci Resolve for finishing. HDRIs from Poly Haven provide lifelike lighting. Topaz Gigapixel AI or Photoshop Super Resolution helps upscale sources.
What image and file formats should I use?
Start with high-res PNG or TIFF sources. Export 16-bit grayscale PNG or OpenEXR depth maps to avoid banding. For delivery, choose GLB/GLTF for web and AR, FBX/OBJ for DCCs and engines, and USD/USDZ for Apple AR workflows.
How does Hyper3D improve depth accuracy and edge quality?
Hyper3D produces perceptually sharp edges and robust occlusion, reducing artifacts during camera moves. Its depth outputs are displacement-ready and mesh-compatible, so cleanup is minimal before you texture and light in your DCC.
Can Vidu AI turn my 3D stills into cinematic videos?
Yes. Vidu AI lets you keyframe push-ins, orbits, and rack focus, add motion blur and depth of field, and output 9:16, 1:1, and 16:9 formats for TikTok, Instagram Reels, YouTube, and more—fast enough for A/B testing.
What is the recommended step-by-step workflow?
Clean and denoise the source image, run Hyper3D to generate a 16-bit depth map, convert depth to displacement or mesh in Blender, refine geometry and UVs, build PBR textures, light with an HDRI plus key/fill/rim, set camera motion, then export GLB/USDZ or render ProRes for Vidu AI.
How can I optimize lighting for realism and mood?
Begin with an HDRI dome for base realism. Add a three-point setup for shape and separation. Match color temperature to the photo, use area lights for soft shadows, and consider gobos for texture without breaking continuity.
Should I bake textures or use real-time materials?
For web and mobile, baking AO, Normal, and Curvature gives stable looks and lower overhead. In Unreal or Unity, real-time materials enable interactive changes. Use ktx2/Basis compression and mipmaps for fast, clean web delivery.
How do I avoid stretching, noise, and banding in depth-based scenes?
Use 16-bit depth or EXR, add dithering if needed, refine UVs, and add support geometry where depth changes abruptly. Balance render samples with AI denoisers like OptiX, and feather masks to remove haloing at edges.
What export settings are best for web, AR, and video?
For web/AR, export GLB/GLTF with ktx2-compressed textures under 10–20 MB, and USDZ for iOS. For video, master to ProRes 422/4444 or DNxHR, then deliver H.264/H.265 in platform-native aspect ratios. Keep color space consistent through the pipeline.
How do I integrate assets into Unreal Engine and Unity?
Import GLB/FBX, set up PBR materials, and in Unreal pack ORM and enable virtual textures. In Unity HDRP/URP, map channels correctly and profile mobile versus desktop. Use LODs and instancing to maintain performance.
Can I automate batch conversions and renders?
Yes. Use Blender Python scripts for depth-to-mesh, UV unwrap, and texture assignment. In Unreal and Unity, leverage Editor Utility Widgets or C# for batch import and LODs. Queue command-line renders and send sequences to Vidu AI for automated camera passes and aspect variants.
What’s the best way to manage versions and shared assets?
Use Git LFS or Perforce for large binaries. Keep clear naming conventions, semantic versioning, and a shared library with standardized HDRIs, LUTs, materials, and camera presets. A simple wiki documents your pipeline for the team.
How do I publish 3D and video content that ranks in search?
Optimize GLB/GLTF size and meet Core Web Vitals. Add JSON-LD schema like VideoObject and Product. Provide captions, quality thumbnails, descriptive filenames, and alt text. Create 16:9, 1:1, and 9:16 variants, submit sitemaps, and track results with Google Analytics 4 and Search Console.
What are the top use cases for marketers and e-commerce teams?
Turn product photos into interactive spins, AR try-ons, and parallax videos that boost engagement and conversions. Repurpose one scene across PDPs, ads, reels, email banners, and DOOH. With Hyper3D and Vidu AI, teams scale creative while keeping brand looks consistent.
Which camera settings create convincing depth in motion?
Use realistic focal lengths (35–85 mm for portraits), set aperture for tasteful depth of field, and apply filmic tone mapping. Add subtle dolly or orbit moves to showcase parallax without breaking the image’s integrity.
How do I keep colors and contrast consistent across apps?
Maintain linear color where needed, verify gamma and tone mapping, and standardize LUTs and HDRIs across Blender, Unreal, Unity, and Vidu AI. Do quick A/B checks against the source image before final export.
What image resolution should I start with?
Use 3000–6000 px on the long edge for strong displacement and close-ups. High-res sources preserve fine detail in textures and normals, reducing artifacts in parallax-heavy shots.
Can small teams achieve production-ready results with this pipeline?
Absolutely. AI-driven depth mapping and template-driven motion let small teams produce polished 3D and video deliverables fast, iterate for A/B tests, and publish across web, AR, and social with minimal overhead.